Oral Surgery Blog - Statesboro & Swainsboro, GA
Tips, Facts, And The
Latest In Dentistry

The Complete 2025 Guide To Type Of Dental Implants
This guide explains the different type of dental implants and helps you decide which option fits your needs. It’s for anyone with one missing tooth, several missing teeth, or looking for a full-arch solution. You’ll learn what each implant type is, when it’s used, the procedure and recovery, costs, and what to ask at your consultation.
The main type of dental implants explained
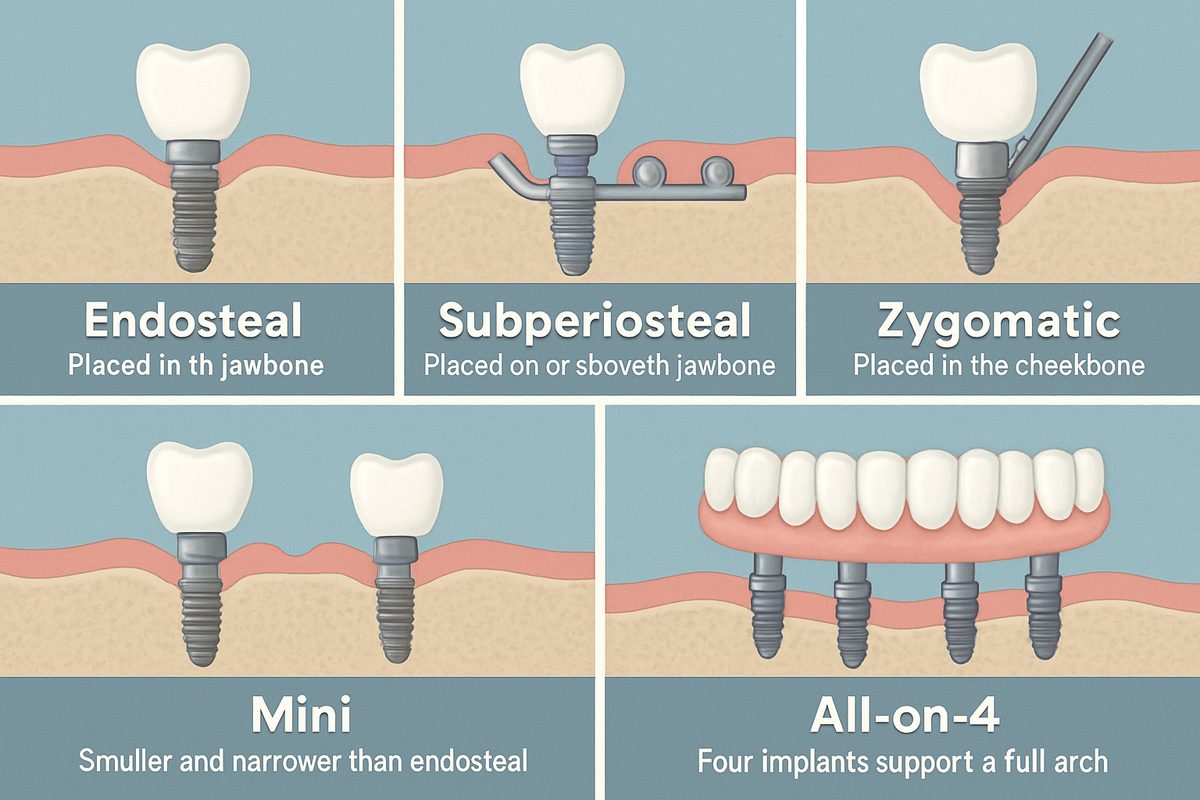
A dental implant is a titanium screw placed into the jawbone to replace a tooth root. The implant supports a crown, bridge, or denture so you can chew and smile naturally. The most common type of dental implants is the root-form (endosteal) implant. This is the standard “type of dental implants” used for single or multiple teeth because it integrates well with bone and offers high success rates.
Other common type of dental implants
Subperiosteal implants
Subperiosteal implants sit on top of the jawbone but under the gum. They are chosen when bone height is too low for root-form implants and grafting is not an option. This type of dental implants is less common today but still useful for specific cases.
Zygomatic implants
Zygomatic implants anchor into the cheekbone (zygoma) instead of the upper jaw. They are used for severe upper jaw bone loss and are reserved for complex reconstructions. Expect a longer surgery and specialized care for zygomatic implants.
Mini dental implants
Mini dental implants are smaller in diameter. They’re often used for narrow gaps, to stabilize dentures, or as temporary supports. Mini implants can be placed faster and with less bone, but they have limits for long-term load and may not be best for large restorations.
Implant-supported dentures / All-on-4 style
Full-arch systems like All-on-4 use multiple implants to support a permanent bridge or denture. This type of dental implants is recommended for patients missing most or all teeth. It can reduce treatment time, and with proper planning patients may leave with provisional teeth the same day.
What determines which type of dental implants you need
Bone quantity and quality
Bone height, width, and density are key. If bone is thin or short, your surgeon may recommend grafting or a different type of dental implants—like zygomatic or subperiosteal—to avoid complex bone work.
Number and location of missing teeth
Single missing tooth = single root-form implant. Several missing teeth may need multiple implants or a bridge. Full-arch loss often points to implant-supported dentures or All-on-4 style options.
Medical history and lifestyle
Smoking, uncontrolled diabetes, certain medications, and age affect healing and implant choice. Your surgeon will review your health to pick the safest, most durable type of dental implants for you.
Aesthetic and functional goals
Treatment aims differ: some want a natural look, others want maximum chewing power. Your priorities help decide between single implants, mini implants, or full-arch solutions.
Procedure steps and recovery by implant type
Most implant paths follow these steps:
- Consultation and 3D scans for planning.
- Preparatory work (extractions or bone grafting if needed).
- Implant placement surgery.
- Healing period (osseointegration) lasting weeks to months.
- Abutment placement and final crown, bridge, or denture.
Mini implants often have faster placements and shorter healing. Zygomatic and complex full-arch surgeries take longer and need specialized teams and imaging.
Pros, cons, and expected lifespan of each type
- Endosteal (root-form): Pros — high success, durable 15+ years; Cons — needs adequate bone, moderate cost.
- Subperiosteal: Pros — works with low bone height; Cons — less common, may be less stable long-term.
- Zygomatic: Pros — avoids grafting for severe upper jaw loss; Cons — major surgery, higher cost, specialist only.
- Mini implants: Pros — less invasive, lower cost, fast; Cons — not ideal for full chewing loads, shorter lifespan for heavy use.
- Full-arch / All-on-4 style: Pros — replaces full arch with fewer implants, can be same-day; Cons — higher upfront cost, maintenance of prosthesis over time.
Typical cost ranges and financing for dental implants
Costs vary by region and treatment complexity. Typical ranges:
- Single root-form implant with crown: $2,000–$6,000+
- Multiple implants and bridges: $6,000–$25,000+
- Full-arch implant-supported solutions (All-on-4 style): $15,000–$50,000+ per arch
Insurance sometimes covers part of procedures, but often not full implant costs. Many practices offer payment plans, third-party financing, or in-house options to spread payments.
How to choose the right implant provider
Look for board-certified oral surgeons or prosthodontists with implant training. Key items:
- Advanced imaging (CBCT 3D scans) and digital planning.
- Experience with the specific type of dental implants you need.
- Clear explanation of risks, timeline, and alternatives.
- Positive patient reviews and before/after cases.
East Georgia Center for Oral & Facial Surgery has board-certified surgeons and 3D planning tools for complex cases, including All-on-4® full-arch solutions at locations in Statesboro and Swainsboro, GA.
Questions to bring to your implant consultation
- Which type of dental implants do you recommend for my situation and why?
- What is the full timeline from start to final restoration?
- Will I need bone grafting or extractions first?
- What are the risks and the success rate for my case?
- How long will the implants and final teeth last, and what maintenance is needed?
- Do you offer financing or payment plans?
- Is there a warranty or follow-up care included?
If you’re deciding which type of dental implants in Statesboro, GA or which type of dental implants in Swainsboro, GA is right for you, schedule a consultation. A detailed exam and 3D scan will clarify options and create a personalized plan to restore your smile and function.